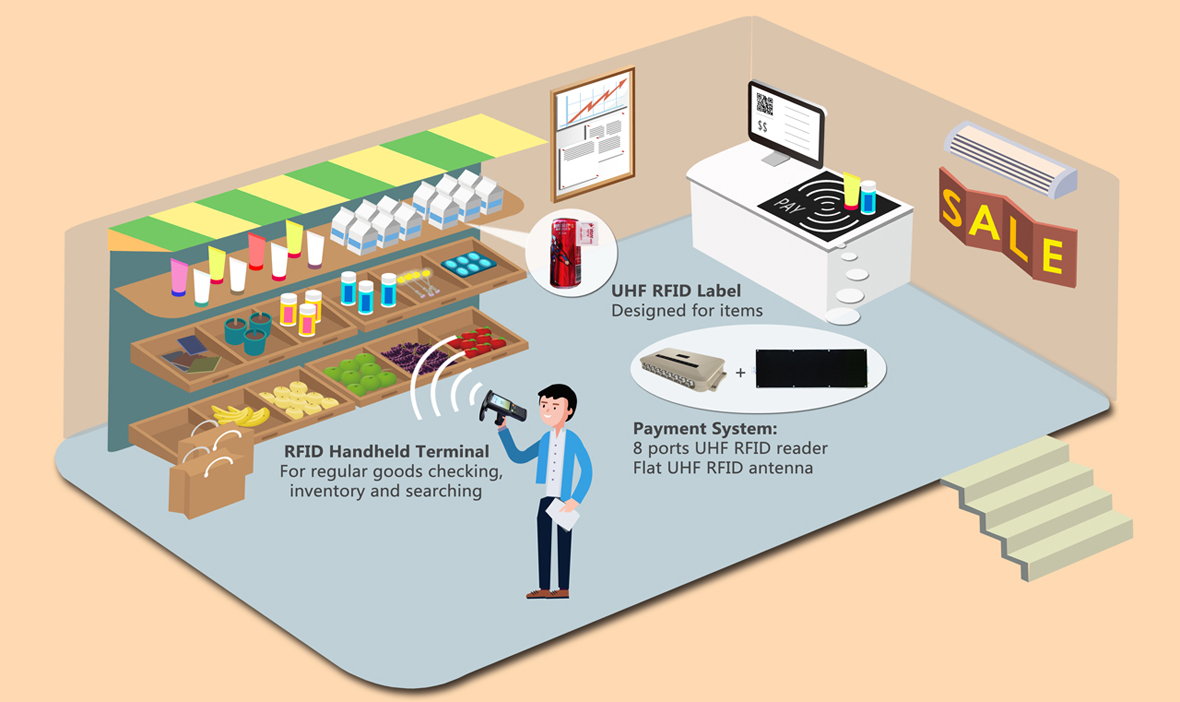
In today’s fast-paced business world, efficient inventory management is crucial for success. Companies constantly seek ways to streamline their operations and reduce costs associated with tracking and maintaining stock levels. So, how can RFID be used to manage inventory?
RFID technology can manage inventory by attaching small tags to items, which can be scanned automatically using radio waves. This allows for real-time tracking, improved accuracy, and reduced labor costs in inventory management. Furthermore, RFID systems can seamlessly integrate with an existing inventory database, providing a comprehensive tracking and managing stock solution.
While this brief answer provides a basic understanding, there’s much more to explore about RFID’s potential in inventory management. Continuing to read will reveal additional benefits, implementation strategies, and real-world examples to help you make informed decisions about incorporating RFID into your inventory systems.
What Are The Key Benefits Of Using RFID For Inventory Management?
Implementing RFID technology for inventory management offers several significant advantages. First and foremost, it dramatically improves accuracy. Unlike traditional barcode systems, RFID tags can be read without line-of-sight, reducing human error and increasing the speed of data collection. This means fewer discrepancies between physical inventory and recorded stock levels, leading to more informed decision-making.
Another major benefit is real-time tracking. RFID systems can continuously monitor inventory movements, providing up-to-the-minute information on stock levels, locations, and environmental conditions. This real-time visibility enables businesses to respond quickly to changes in demand, prevent stockouts, and optimize their supply chain.
Lastly, RFID technology can significantly reduce labor costs. Automated scanning eliminates the need for manual counting and data entry, freeing up staff to focus on more value-added tasks. This increases efficiency and reduces the likelihood of human error, further improving overall inventory accuracy.
How Does RFID Compare To Traditional Barcode Systems?
While RFID and barcode systems are used for inventory management, they differ in several key aspects. Barcodes require line-of-sight scanning and can only be read one at a time, whereas RFID tags can be scanned simultaneously and without direct visual contact. RFID systems can process large quantities of inventory much faster than barcode systems.
RFID tags also have a higher data capacity than barcodes. They can store more detailed information about each item, including manufacturing, expiration, and maintenance history. This additional data can be invaluable for industries with complex inventory needs, such as pharmaceuticals or electronics.
However, it’s worth noting that RFID systems generally have a higher initial cost compared to barcode systems. The tags are more expensive, and implementing RFID readers and software requires a more significant upfront investment. Despite this, many businesses find that the long-term benefits of RFID outweigh the initial costs, especially for large-scale operations.
What Industries Can Benefit Most From RFID Inventory Management?
While RFID technology can benefit various sectors, specific industries stand to gain the most from its implementation. Retail is one such industry where RFID can revolutionize inventory management. It allows for quick and accurate stock counts, reduces shrinkage, and enables seamless omnichannel experiences by providing real-time inventory visibility across all sales channels.
RFID can also significantly impact the healthcare industry. Hospitals and pharmacies can use RFID to track medications, ensure proper storage conditions, and reduce the risk of expired drug administration. It can also track medical equipment, improving utilization rates and reducing losses.
In manufacturing, RFID can enhance supply chain visibility and streamline production processes. It can track raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished goods throughout the manufacturing cycle, helping to identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows. This level of tracking is particularly valuable in industries with complex assembly processes, such as automotive or aerospace manufacturing.
How Can Businesses Implement RFID For Inventory Management?
Implementing RFID for inventory management requires careful planning and execution. The first step is to thoroughly assess your current inventory system and identify areas where RFID could benefit most. This might involve analyzing pain points in your existing processes, such as frequent stockouts or inventory discrepancies.
Next, you’ll need to choose the right RFID system. This includes selecting appropriate tags (passive or active), readers, and software. Consider factors such as the size and type of items you’re tracking, the environment they’ll be stored in, and the level of detail you need to capture.
Once you’ve selected your system, it’s crucial to integrate it with your existing inventory management software and other business systems. This integration ensures that the data collected by RFID can be used effectively across your organization. Many businesses find starting with a pilot program in one area of their operations helpful before rolling out RFID across their entire inventory.
Finally, remember training. Your staff must understand how to use the new RFID system effectively. This includes the technical aspects of using the equipment and interpreting and acting on the data it provides. Proper training can differentiate between a successful implementation and a costly misstep.
What Are The Potential Challenges Of Using RFID For Inventory Management?
While RFID offers numerous benefits for inventory management, it has its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the initial cost of implementation. As mentioned earlier, RFID systems can be more expensive to set up than traditional barcode systems. This can be a significant barrier for small businesses or those with tight budgets.
Another challenge is the potential for interference. RFID tags use radio waves to communicate, which can be disrupted by metal objects or liquids. This can be problematic in environments with a lot of metal shelving or products or in industries that deal with liquid products. Careful planning and testing are required to ensure reliable performance in these conditions.
Privacy concerns can also be an issue, particularly in retail environments. Some consumers need help with the potential for RFID tags to be used to track their purchases or movements. While these concerns are often unfounded (as most RFID tags used in retail are passive and have a minimal range), businesses need to be prepared to address these worries and ensure they’re using RFID technology responsibly.
Lastly, data management can be a challenge with RFID systems. These systems generate vast amounts of data, which can be overwhelming if not properly managed. Businesses need robust data analysis tools and processes to turn this raw data into actionable insights. With this, the potential benefits of RFID can be recovered in a sea of unprocessed information.
Taking the Next Step with RFID Inventory Management
Now that you understand the potential of RFID in inventory management, it’s time to take action. Consider conducting a cost-benefit analysis for implementing RFID in your business operations. This analysis should consider your current inventory challenges, the potential improvements RFID could bring, and the costs associated with implementation. By doing this, you’ll be able to decide whether RFID is the right solution for your inventory management needs.
Keep an eye for more news & updates on InternalInSider!